Best practices: Working with project filters
Filters enable targeted queries based on attributes such as severity, package ecosystems, dependency resolution, and platform source.
This guide explains how filters work, how to apply and combine them effectively, and provides practical examples to support triage, audit, and reporting workflows across large codebases.
Access project filters
Perform the following steps to apply filters to the project list.
- Select Projects from the left sidebar.
- Filter your projects using the list of available filters in the filter bar.
- Toggle the Advanced option in the filter bar to apply API-style filters.
You can combine multiple filters to create more specific searches and narrow down the project list based on multiple criteria.
How filters work
Each filter consists of three parts.
- Field: The attribute to be filtered (for example,
Package CountandPlatform Source). - Operator: The comparison logic (for example,
equals,greater than, andin). - Value: The target value to evaluate (for example,
npmand100).
Project filters use standard comparison operators to evaluate criteria. See Filter operators for detailed information about available operators and their usage.
When you apply multiple filters, the system combines them using logical AND operations across filters for different fields and logical OR operations across filters for the same field.
For example:
- Filter 1:
Package Ecosystems contains: npm - Filter 2:
Platform Source in: GitHub - Filter 3:
Package Count: greater than 1 - Filter 4:
Reachability Analysis Status greater than or equal to: 90%
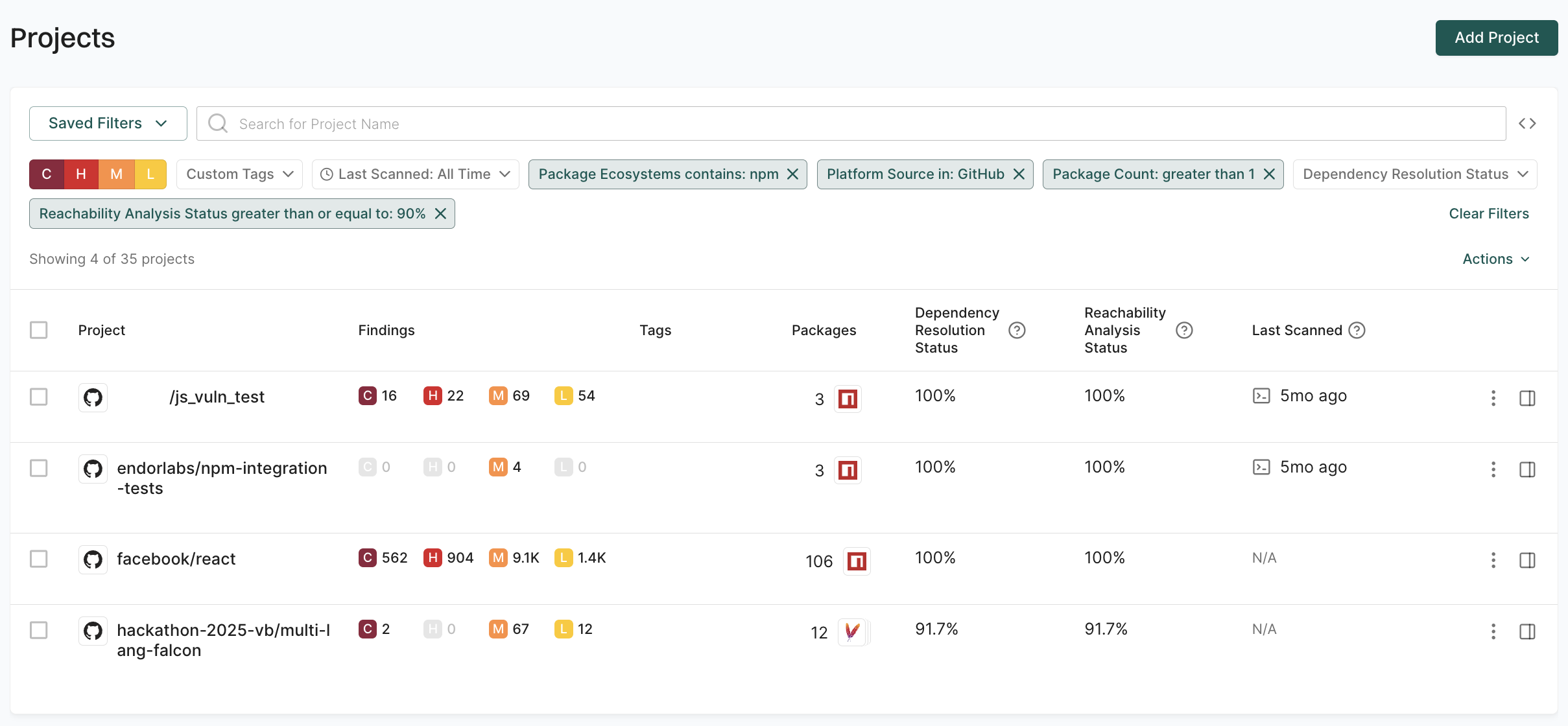
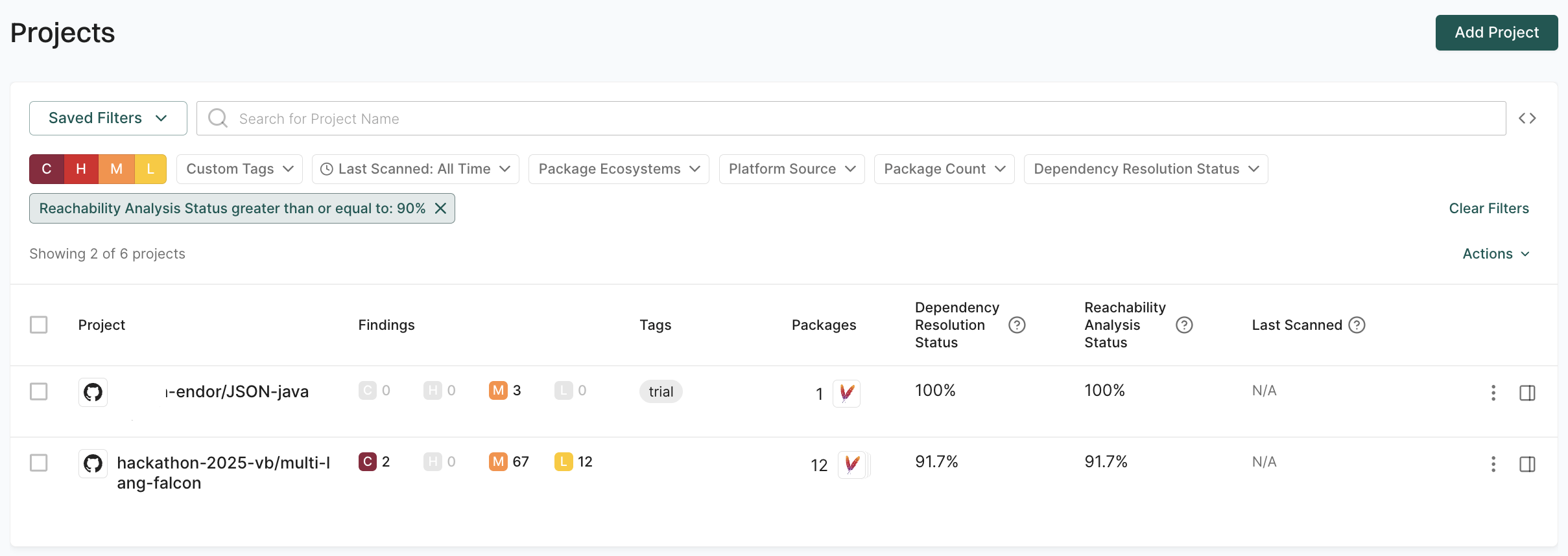
This combination returns only projects that use npm packages, are from GitHub, have more than one package, and have a reachability analysis status of at least 90%.
Filter implementation techniques
You can use the following filter types to manage your projects effectively.
- Preset filters: Use predefined UI-based filters to quickly segment projects by common attributes.
- Filter projects using API: Use advanced syntax for complex queries and logical combinations.
Preset filters
The following examples demonstrate how to apply preset filters for common project scenarios.
Filter projects by custom tags
Use custom tags to filter projects based on environment or predefined labels assigned during project initialization or scan configuration.
For example, to view only projects related to SAST, use the Custom Tags contains: sast filter.
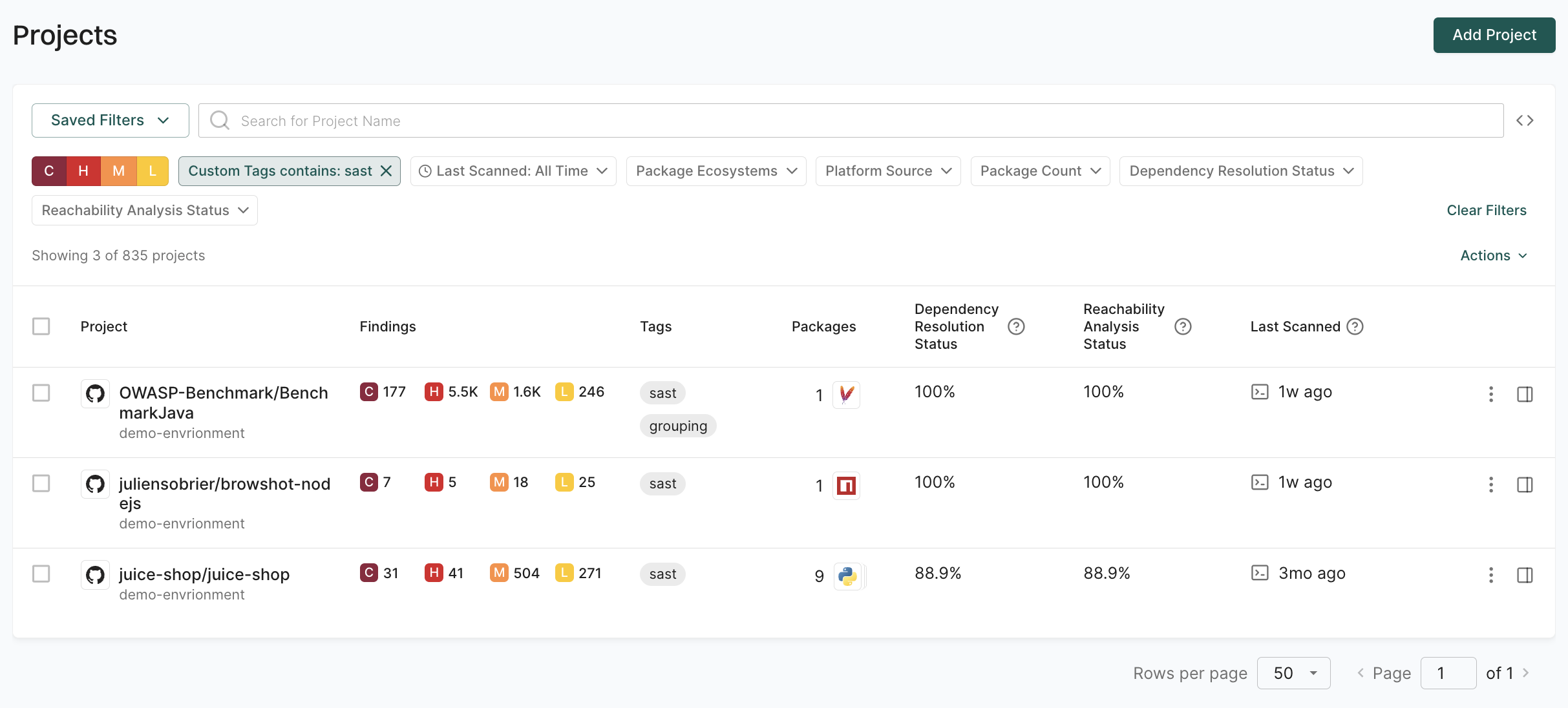
Filter projects by findings severity
Prioritize remediation efforts by filtering projects based on the severity of security findings. You can select from Critical (C), High (H), Medium (M), or Low (L) severity filters to target different priority levels.
For example, to identify projects with critical findings, select the C filter.
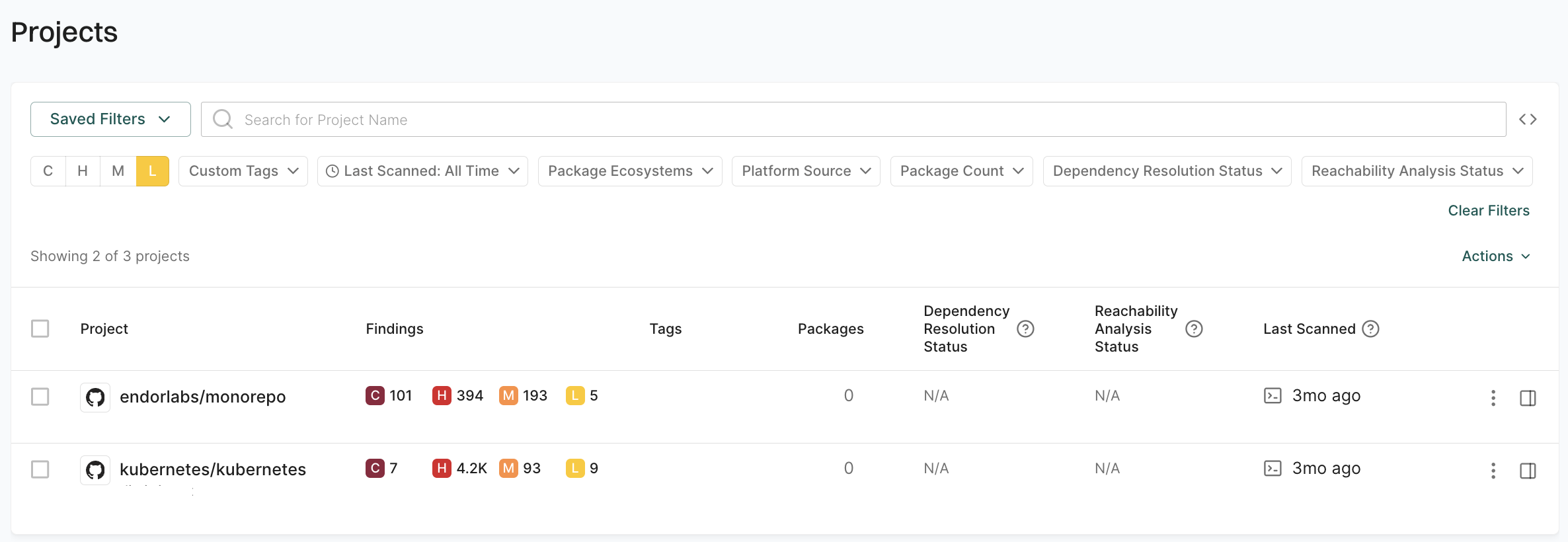
Filter projects by package ecosystem
Use package ecosystem filters to segment projects by programming language or package management system for targeted security policies such as stricter vulnerability thresholds for JavaScript projects or specific license compliance checks for Java applications.
For example, to focus on PHP projects for a security assessment, use the Package Ecosystems contains: Packagist filter.
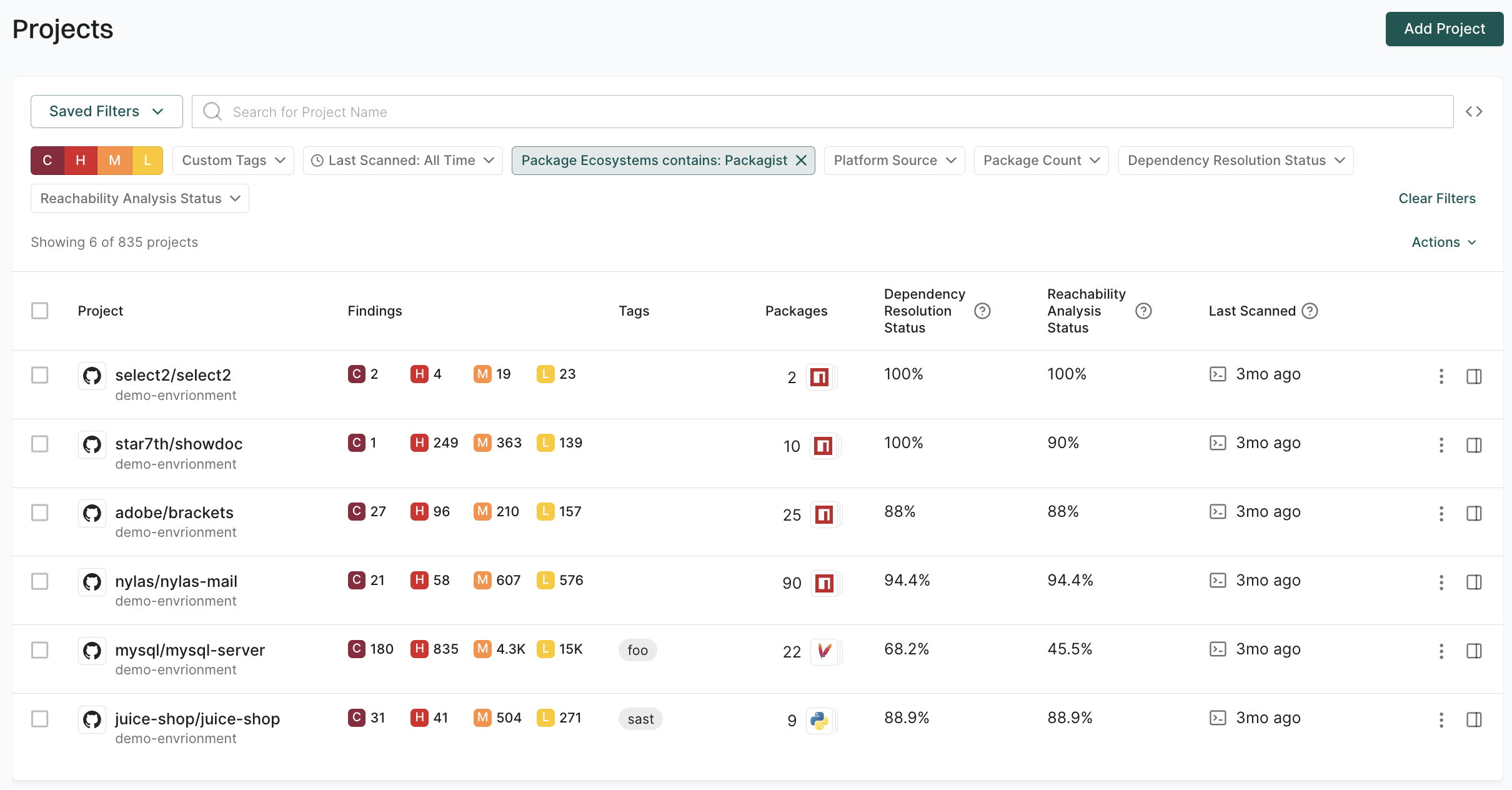
Filter projects by source platform
Use platform source filters to segment projects by their source platform and correlate findings with platform-native security tools like GitHub’s Dependabot alerts or GitLab’s vulnerability scanning.
For example, to identify projects analyzed from GitLab, use the Platform Source in: GitLab filter.
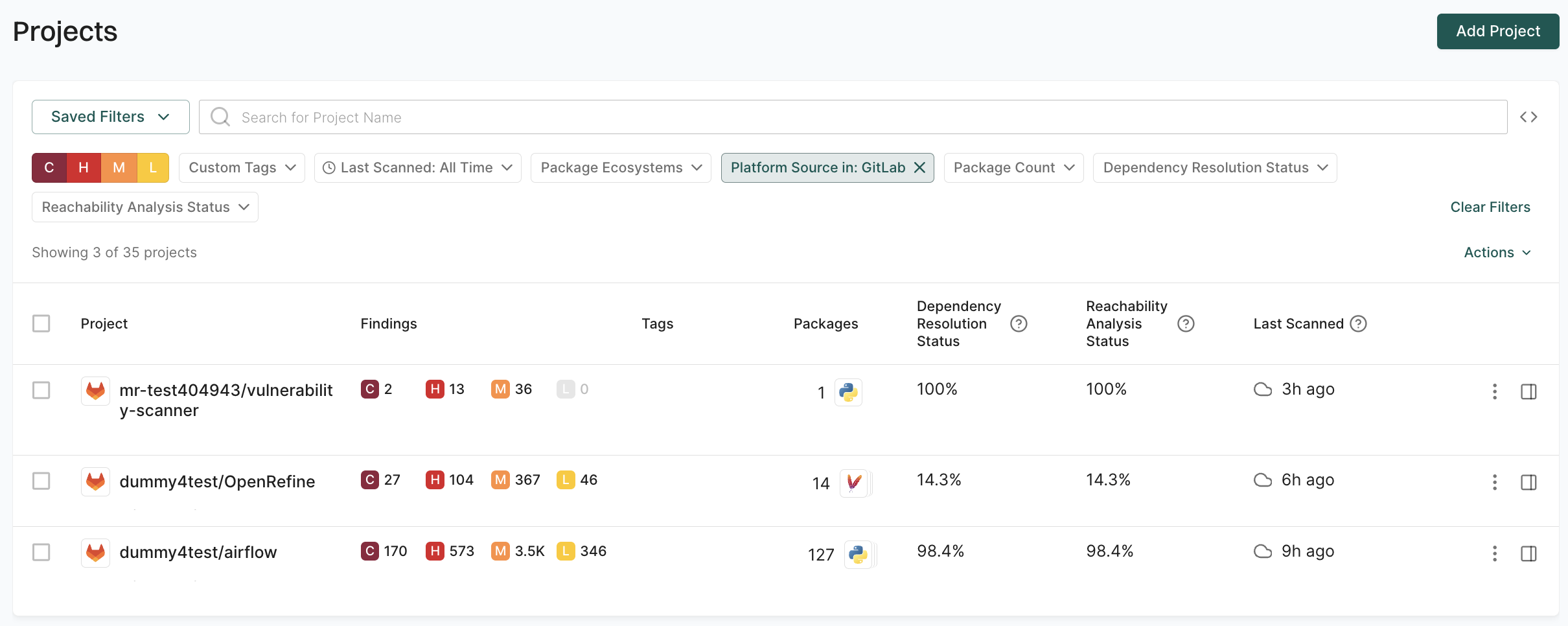
Filter projects by dependency resolution quality
Use dependency resolution status to identify projects with resolution issues that impact security analysis accuracy. You can filter by a single value or a range of percentages.
For example, to identify projects with poor dependency resolution, use the Range filter to find projects with Dependency Resolution Status greater than 0% and less than 50%.
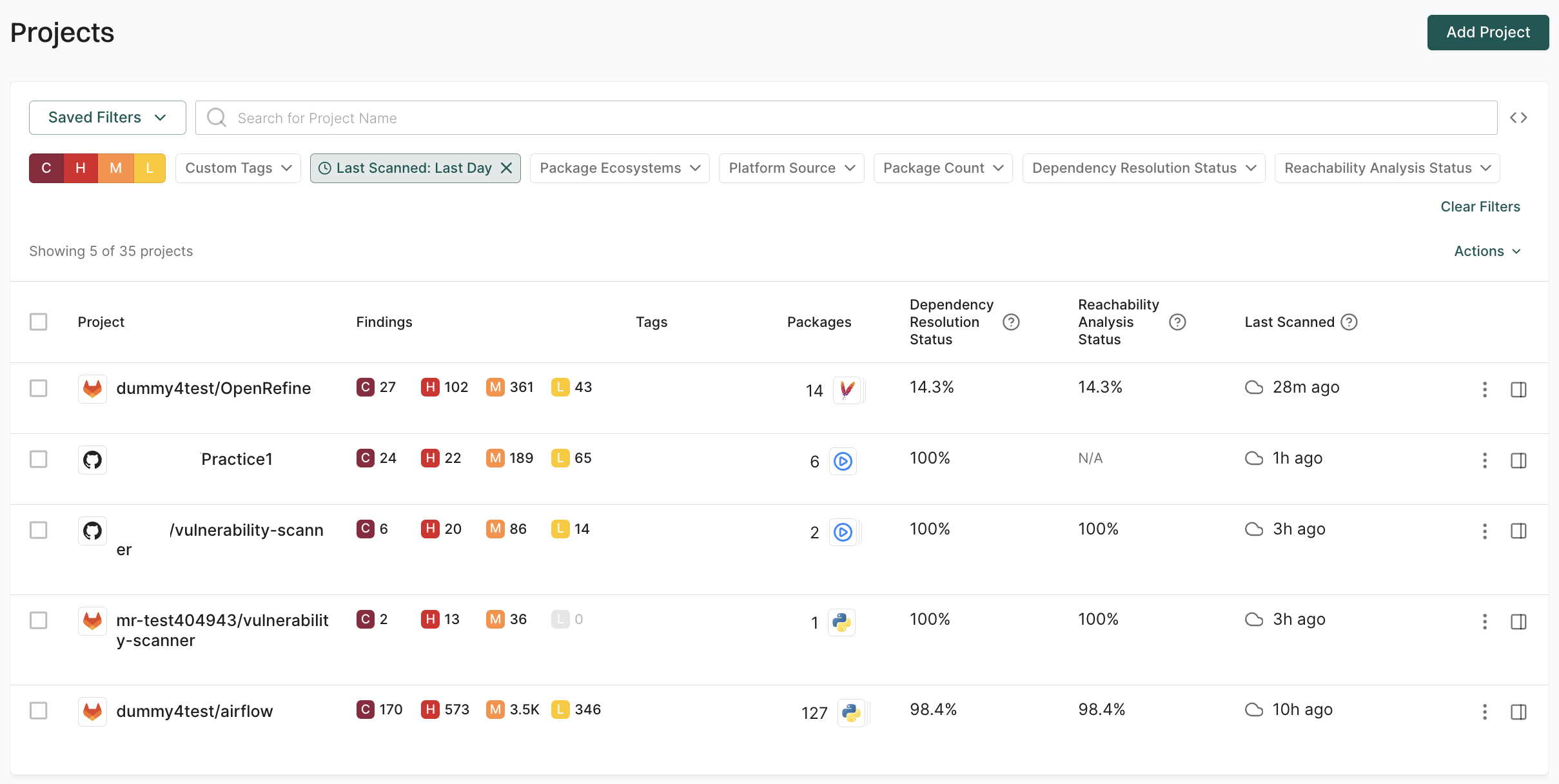
Filter projects by scan timestamp
Use last scanned filters to identify projects with stale security data that require fresh scans for current security posture. You can select from predefined time ranges or use the calendar to select a specific date.
For example, to identify projects scanned within the last 24 hours, use the Last Scanned: Last Day filter.
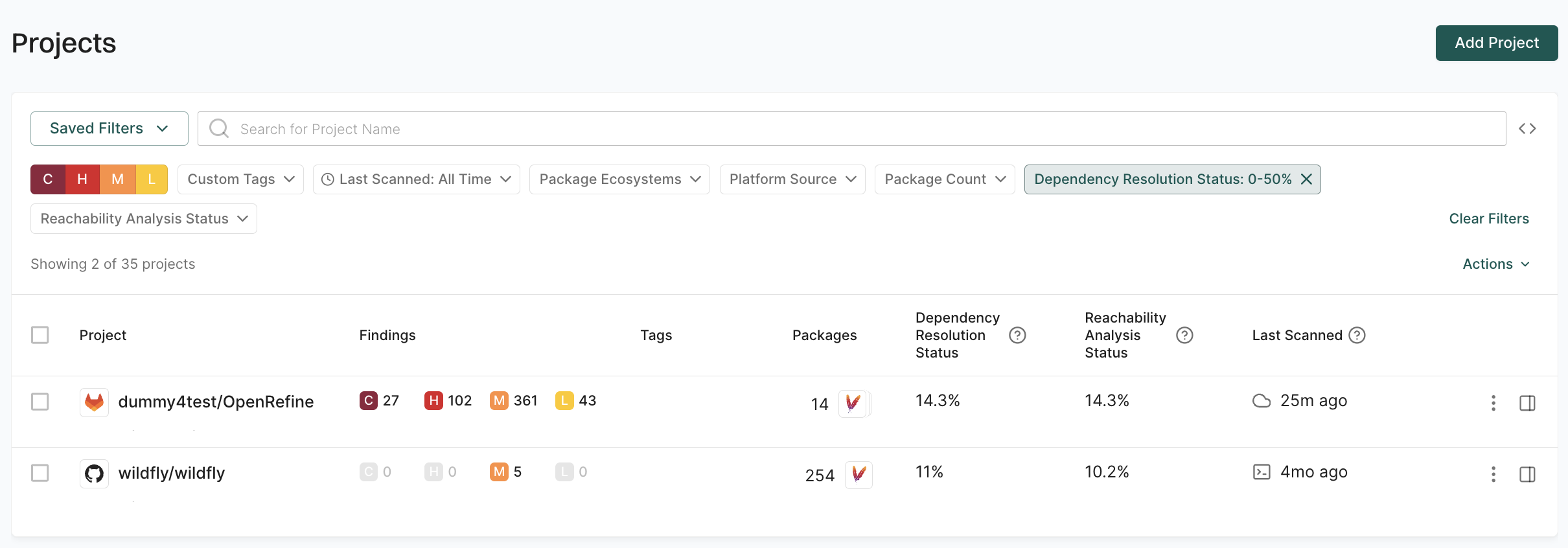
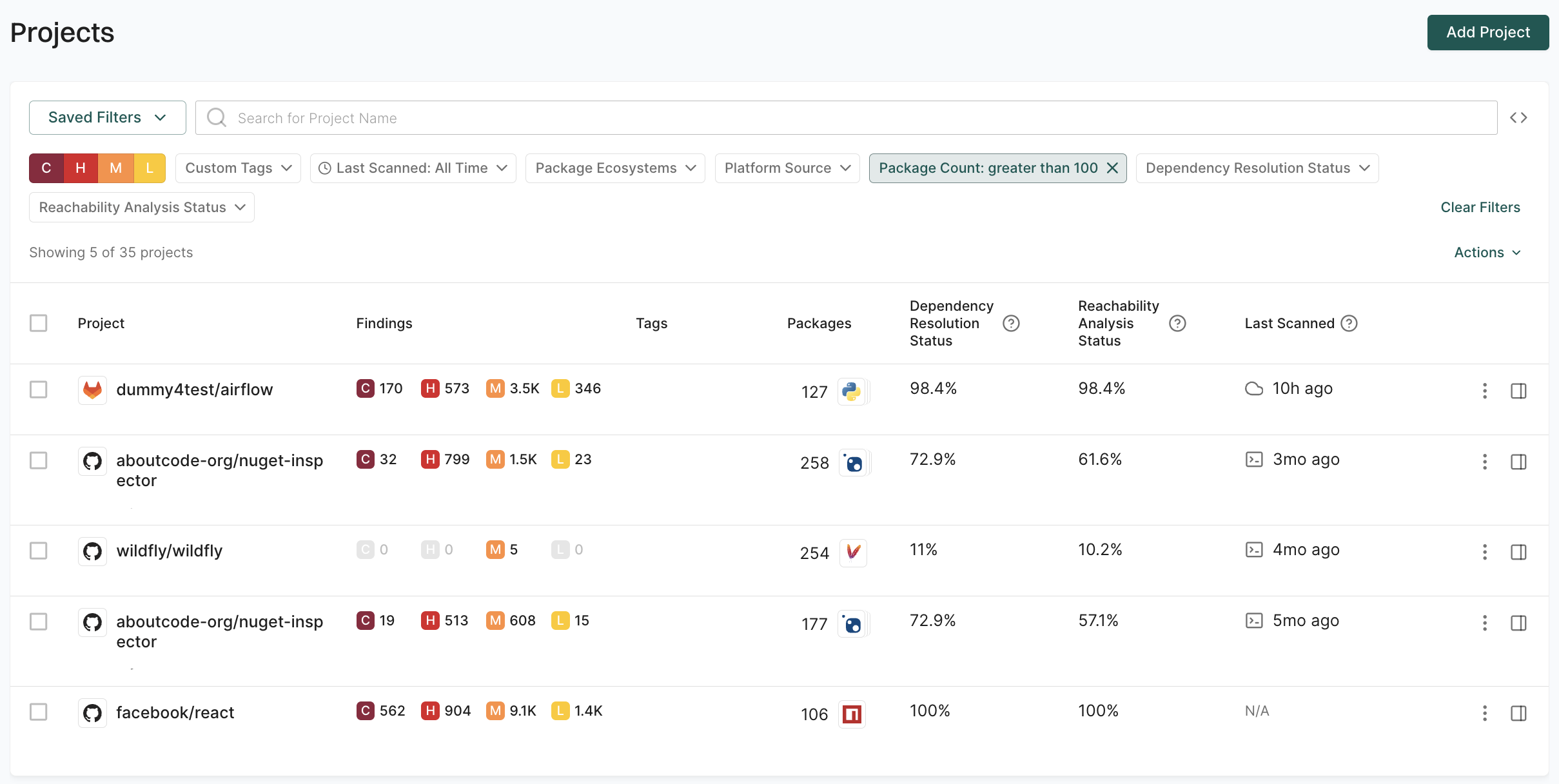
Filter projects by complexity
Identify projects based on their size and complexity, which may require different levels of security attention and resources.
For example, to focus on large projects with extensive dependency trees, use the Package Count: greater than 100 filter.
Filter projects by reachability analysis status
Use reachability analysis status to identify projects based on the success rate of call graph generation and reachability analysis. You can filter by a single value or a range of percentages.
For example, to identify projects with successful reachability analysis, use the Reachability Analysis Status greater than or equal to: 90% filter.
Filter projects using API
For complex queries, use the advanced filter syntax to combine multiple attributes and apply logical operators.
The following table lists the available attributes for project filters.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| Project UUID | Filters projects by their unique identifier. |
| Name | Filters projects by the display name of the project. |
| Custom Tags | Filters projects by custom tags set during project setup or scan configuration. |
| Last Scanned | Filters projects based on the timestamp of the last successful scan. |
| Package Count | Filters projects by the total number of packages resolved in the project. |
| Package Ecosystems | Filters projects based on the language-specific package ecosystems they use. |
| Dependency Resolution Status | Filters projects by the percentage of resolved dependencies in the project. |
| Reachability Analysis Status | Filters projects based on the success rate of reachability analysis through call graph generation. |
| Critical Findings Count | Filters projects based on the number of critical-severity findings in the project. |
| High Findings Count | Filters projects based on the number of high-severity findings in the project. |
| Medium Findings Count | Filters based on the number of medium-severity findings in the project. |
| Low Findings Count | Filters projects based on the number of low-severity findings in the project. |
| Dismissed Findings Count | Filters projects based on how many findings were manually dismissed by users. Useful for reviewing triaged issues. |
| Total Findings Count | Filters projects based on the total number of findings detected in a project. |
| Platform Source | Filters projects based on source platform and helps narrow results by version control origin such as GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket. |
API filter use cases
The following examples demonstrate how to combine these attributes for common security and compliance workflows.
Identify high-risk GitHub projects
Find GitHub projects with more than 5 critical findings and a reachability analysis status below 80%.
spec.platform_source == "PLATFORM_SOURCE_GITHUB" and spec.finding_counts.critical > 5 and spec.package_coverage.call_graph_success_rate < 0.8
Audit stale projects with risks
Identify projects not scanned in the last 7 days that still have outdated dependencies.
spec.last_scanned < now(-168h) and spec.dependency_counts.outdated > 0
Identify projects with low dependency resolution quality
Find projects where dependency resolution is below 90%, which may indicate incomplete security analysis.
spec.package_coverage.success_rate < 0.9
Find large projects with high vulnerability density
Identify projects with more than 100 total packages that also have a high number of critical vulnerabilities.
spec.package_coverage.total > 100 and spec.vulnerability_counts.total.critical > 20
Audit projects with high triaged findings
Find projects where more than 50 findings have been dismissed, useful for auditing triage quality.
spec.finding_counts.dismissed > 50
Triage critical vulnerabilities by ecosystem
Focus on npm projects with a high number of critical vulnerabilities.
spec.package_coverage.ecosystems contains ECOSYSTEM_NPM and spec.vulnerability_counts.total.critical > 10
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Thanks for the feedback. Write to us at support@endor.ai to tell us more.
Thanks for the feedback. Write to us at support@endor.ai to tell us more.